An acoustic lens for displacement-free sectorial inspection of pipes with ultrasonic phased arrays
Dec 1, 2025· ,,,,·
0 min read
,,,,·
0 min read
Gustavo P. Pires
Equal contribution
Thiago E. Kalid
Equal contribution
,Tatiana A. Prado
Vinícius L. Costa
Gabriela R. Pereira
Thiago A. R. Passarin
Daniel R. Pipa
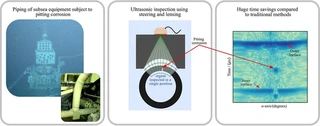 Image credit: Pires et al. 2025
Image credit: Pires et al. 2025Abstract
Pipes that transport acidic fluids are prone to pitting corrosion, which causes well-localized thickness loss. The detection and measurement of these small flaws via ultrasonic non-destructive testing (UT) requires a fine sampling of the surface of the pipe, which is time-consuming and expensive, especially in places where the inspections require dedicated infrastructure, such as subsea facilities. In this work, we present an acoustic lens that, used with a UT phased array system capable of beam steering, allows for the inspection of large sections (e.g., 90 degrees) of a submerged pipe without any mechanical displacement. The mathematical formulation is derived from geometrical optics, and algorithmic procedures to compute customized delay laws are provided. Practical aspects of the manufacturing and assembly of the device are also described. Spatial resolutions of a prototypical manufactured lens on three axes are assessed on a 140 mm-diameter pipe and compared to those obtained with a moving single-element transducer, showing competitive resolutions. Measurements of the remaining thicknesses of 1.5 mm-diameter machined flaws performed with the device provided a mean absolute error of 19% of one wavelength and maximum absolute error of 51% ($\lambda = 1.18$ mm). The results demonstrate the potential of the proposed concept to replace single-element UT, significantly reducing inspection time by removing mechanical displacement otherwise necessary during an axial sweep.
Type
Publication
NDT & E International
Pipe Inspection
Pitting Corrosion
Phased Arrays
Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement
Acoustic Lens
Ray-Tracing
Authors

Authors
Master’s Student
Thiago E. Kalid is a master’s student at the Laboratory of Statistical Signal Processing and Inverse Problems (Brazil).
Authors
Authors
Authors
Authors
Authors